1. Japan has lost its way with hydrogen
Image credit ykanazawa1999 JHFC Senju Hydrogen Station
Six years ago, Japan was the first country to set out a hydrogen strategy and allocate significant subsidies to infrastructure to displace battery powered electric vehicles.
Problems such as carbon fuelled hydrogen plants, disconnected Government policy, lack of industry targets and a backward strategy according to some have led to performance “far below its main goal of increasing uptake of fuel cells and fuel cell vehicles, and the hydrogen stations built across the country have seen little use,” says a report by the Renewable Energy Institute, Tokyo. Experts say the main problem is that Japan tried to run its new strategy on old fossil fuel principles.
In an apparent bid to save face Japan is pedalling the idea of co-firing green ammonia (produced from its clean hydrogen stations) with coal in Asian coal plants (converting coal plants to run on ammonia) as a safe strategy. In fact, co-firing ammonia with coal is more expensive and produces more C02 than a fossil gas plant.
Nevertheless, undeterred the Japanese Government has announced a review of the plan to come out in May. The main goal is to increase output from 2 million tonnes to 12 million by 2040.
2. Singapore business incentives and schemes

Credit Singapore by Christopher Chan via Flickr
A range of incentives and schemes are available in Singapore for companies considering expansion or growth.
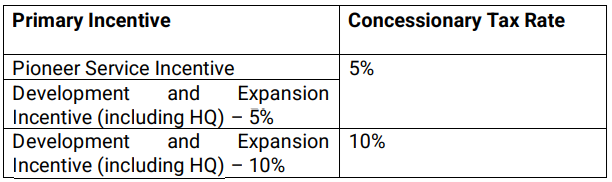
- Pioneer Certificate Incentive (PC) & Development and Expansion Incentive (DEI): Recipients are eligible for a corporate tax exemption on income derived from the manufacturing of the Pioneer product(s).
- Finance & Treasury Centre (FTC) Incentive: Concessionary Tax Rate: 10%
- Tech@SG Programme: employment scheme
- Pass: startup visa
- Intellectual Property (IP) Development Incentive (IDI): Concessionary tax rate
Read more https://www.edb.gov.sg/en/how-we-help/incentives-and-schemes.html
3. US Japan trade deal

Image credit 内閣官房内閣広報室 via Wikimedia Commons
The US and Japan have signed a trade deal that could potentially open up the $7,500 electric vehicle subsidy to Japanese manufacturers.
The deal is specifically focused on rare minerals required for the manufacture of electric vehicles being lithium, nickel, cobalt, graphite and manganese. The agreement removes “bilateral export restrictions.”
The $7,500 credit is enacted by the Inflation Reduction Act. Half of the credit is based on assembly in the US. The other half is based on critical materials rules of origin which must be the US or a trusted other country i.e. one with a trade deal with the US.
Trade Horizons advisors are market entry experts: our team of in-country experts assist companies to export, import and enter new locations by using strategies that have stood the test of time and evidence-based advice. Trade Horizons assists companies to plan to distribute and deliver goods or services to a new target market. Contact one of our experts today.
4. India Russia trade deal

Image credit President of Russia via Wikimedia Commons
India and Russia are negotiating a free trade agreement in a surprising twist of events. Relations between the two countries have received increased attention since the war in Ukraine started.
Whilst the rest of the world has been calling for India to take a step back from Putin’s regime, it seems India has taken the opposite approach.
India’s imports from Russia quadrupled last year to $46.33 billion mainly in oil.
Russa is part of the Putin-led ‘Eurasian Economic Commission’ consisting of Armenia, Belarus and Kazakhstan.
Russia displaced Iraq as the world’s top producer of crude oil last month.
Russia is also negotiating a nuclear power plant in Bangladesh and exporting oil to Pakistan.
5. Germany EU Blue Card Changes Explained

Credit Austria by Joss Woodhead via Unsplash
The EU has revised its blue card requirements. The Blue Card is a residence / work permit required of migrants to live and work in Europe.
The revisions stem from a reported shortage in skilled labour. German language is no longer required. Validity has been increased to 3 years, salary threshold has been lowered and other changes make it easier to apply for a blue card. Read more https://www.schengenvisainfo.com/news/germany-eu-blue-card-changes-explained/
6. Vietnam targets agriculture exports

Credit Vietnam by Doan Tuan via Unsplash
The Vietnamese Government has released targets of $25 billion investment into the agriculture sector by 2030. The statement is heavily reliant on the US with 5 billion in US loans and 1 billion in US grants targeted.
It aims to grow fisheries exports to 70 billion USD in the same time.
Vietnam has 6 bilateral and 8 multilateral trade agreements. Vietnam is the world’s third largest rice exporter. Before 2019 China was by far Vietnam’s biggest importer of rice. In 2019 Chinese imports plummeted and never regained due to China increasing the import tax on glutinous rice from 5% to 50% and increased restrictions on broken rice. The Philippines is now Vietnam’s largest importer of rice.
7. IMF and China united in Friendshoring swipe
The International Monetary Fund and China have taken swipes at the West’s Friendshoring policies.
US cutting off China reduced hot money flows and bank lending by around 15 per cent between the two enemies. Friendshoring reduces political uncertainty and supply chain risk amongst other benefits.
In a seemingly coordinated effort a Chinese bank worker recently took a swipe at friendshoring, presumably lamenting economic loss caused by the US isolating China and relying on friendly countries instead.
Western countries are increasingly diverting supply chains away from China as Beijing’s threats to Taiwan increase.
At the recent G7 meeting members pledged to rely more on low and middle income countries which would allow western countries to reduce reliance on China even more.
Featured image credit ykanazawa1999 JHFC Senju Hydrogen Station