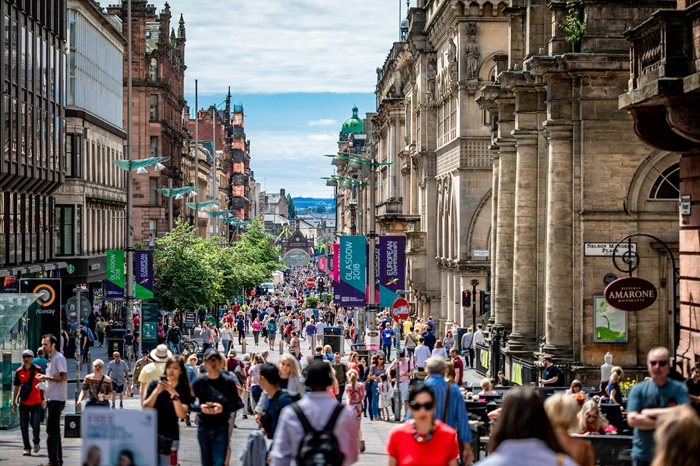
1. Glasgow: Europe’s Premier Destination for Foreign Investment
In a resounding victory, Glasgow has secured its position as Europe’s number one large city for attracting overseas investment. The prestigious accolade, bestowed by world-leading business experts at fDi Intelligence, places Glasgow ahead of formidable contenders such as Bilbao, Porto, Dusseldorf, and Gothenburg.
A Strategic Triumph
What sets Glasgow apart? It’s not just the stunning architecture or the vibrant cultural scene. Rather, it’s the city’s unwavering commitment to strategic excellence. Glasgow’s innovative approaches and remarkable ability to secure foreign investment have propelled it to the top spot. The city’s partnerships between government, academia, businesses, and the community have been instrumental in creating an environment conducive to growth and prosperity.
Investment in Innovation
Over the past 18 months, Glasgow has secured hundreds of millions of pounds in funding, fuelling the emergence of cutting-edge sectors across the city region. From tech to the green economy, from the space industry to advanced manufacturing, Glasgow is at the forefront of innovation. These investments not only create high-quality jobs but also enhance the global reputation of the city.
A Rising Star
In addition to its foreign direct investment strategies, Glasgow shines in other areas too. The city ranks fifth for connectivity and tenth for business friendliness. This comprehensive performance places Glasgow firmly on the map as a rising star in the European investment landscape.
A Collective Effort
City Council leaders, businesses, and universities celebrate this momentous achievement. Councillor Susan Aitken, Leader of Glasgow City Council, expressed her delight: “Recent years have seen the emergence of significant sectors, and these will drive Glasgow’s future growth and high-skilled jobs.”
As Glasgow continues to attract global attention, it stands as a testament to the hard work and collaboration of all partners involved. The world increasingly recognises Glasgow as a city of opportunity, where investment thrives, and prosperity knows no bounds.
2. Uruguay’s Dual Energy Path: Oil & Gas vs. Green Hydrogen

Karan Chaudhari Unsplash
Uruguay, a nation nestled between Brazil, Argentina, and the South Atlantic Ocean, has long been a trailblazer in clean energy. With an electricity grid powered by 95% low-carbon sources, including hydropower, wind, biomass, and solar, it has achieved what most countries aspire to: a successful energy transition.
However, recent developments have sparked a fascinating twist in Uruguay’s energy narrative. Despite its unwavering focus on sustainability, the country is now venturing into offshore oil and gas exploration. Let’s delve into this intriguing dichotomy:
The Green Hydrogen Vision
Uruguay’s commitment to decarbonisation remains steadfast. Having nearly accomplished its first energy transition, the government is now embarking on a second phase—one that involves electric mobility and green hydrogen production. The goal is clear: to lead the charge in sustainable energy solutions.
The Unexpected Plot Twist
Uruguay’s exploration activities date back to the 1970s, but until recently, no significant hydrocarbon deposits had been found. Then, a seismic shift occurred more than 7,000 kilometers away. TotalEnergies and Shell’s discovery of 11 billion barrels of oil off the coast of Namibia sent ripples across the Atlantic. Why? Because millions of years ago, Uruguay and Namibia were connected, sharing similar geological characteristics. This newfound connection doubled the probability that Uruguay’s offshore areas might indeed harbor oil or gas resources.
Investor Interest Ignited
Energy firms, once hesitant, now flock to Uruguay with renewed interest. The Namibian discoveries de-risked Uruguay’s exploration profile, prompting a “stampede” among major players. Companies like Shell, Apache, and YPF have secured licenses for Uruguay’s offshore acreage, signalling a seismic shift in the country’s energy landscape.
Balancing Act
On the surface, Uruguay’s foray into hydrocarbons seems at odds with its green ambitions. However, there’s a method to this apparent madness. Beyond replacing its daily oil imports, Uruguay views an offshore hydrocarbons industry as a strategic stepping stone toward advancing its green hydrogen goals. It’s a delicate balancing act—one that could redefine Uruguay’s energy trajectory.
As the nation treads this dual path, it stands at the crossroads of tradition and innovation. Will oil and gas discoveries propel Uruguay’s economy forward, or will green hydrogen remain the ultimate beacon of progress? Only time will reveal the outcome, but one thing is certain: Uruguay’s energy story is far from over.
3. Chile’s Green Hydrogen Odyssey: Paving the Path to Net Zero

Olga Stalska Unsplash
In the vast expanse of the Atacama Desert, where the sun blazes relentlessly and the winds whisper secrets across the arid landscape, Chile is penning a new chapter in its energy saga. This chapter revolves around a seemingly unassuming element: hydrogen. But not just any hydrogen—green hydrogen.
The Hydrogen Revolution
Hydrogen, the simplest atom in our universe, has captured the imagination of scientists, policymakers, and visionaries alike. Its allure lies in its potential to revolutionise our energy landscape. And in Chile, where the sun’s embrace is unwavering and the winds dance with fervour, green hydrogen emerges as a beacon of hope.
Chile’s Unique Position
Chile, though modest in its global greenhouse gas emissions (contributing just 0.3% to the total), harbours immense potential. Its northern deserts boast the highest solar irradiance on Earth, while the southern Patagonian winds sweep across pristine landscapes. Here lies the canvas for a dual transformation: one that balances tradition with innovation, and fossil fuels with renewable energy.
The National Green Hydrogen Strategy
In November 2020, Chile unveiled its National Green Hydrogen Strategy—a roadmap to harness the power of hydrogen for a sustainable future. Here are the key brushstrokes:
1. Electrolysis Capacity:
By 2025, Chile aims to have 5 gigawatts of electrolysis capacity operational and under development. This monumental leap will unlock the potential for large-scale green hydrogen production.
2. Cost Leadership:
The audacious goal? To produce the world’s cheapest green hydrogen by the end of this decade. Chile’s abundant renewable resources—sun, wind, and water—position it as a frontrunner in cost-efficient hydrogen production.
3. Global Exporter:
By 2040, Chile envisions itself among the top three exporters of 100% green hydrogen. Imagine ships laden not with oil or coal, but with the promise of a cleaner, more sustainable energy future.
A Balancing Act
Chile’s journey toward net zero is a delicate dance. As it explores offshore oil and gas reserves, it simultaneously invests in green hydrogen. The desert sun and Patagonian winds bear witness to this dual commitment—a tightrope walk between tradition and transformation.
4. World’s Largest Ocean-Based Carbon Removal Plant to Be Built in Singapore
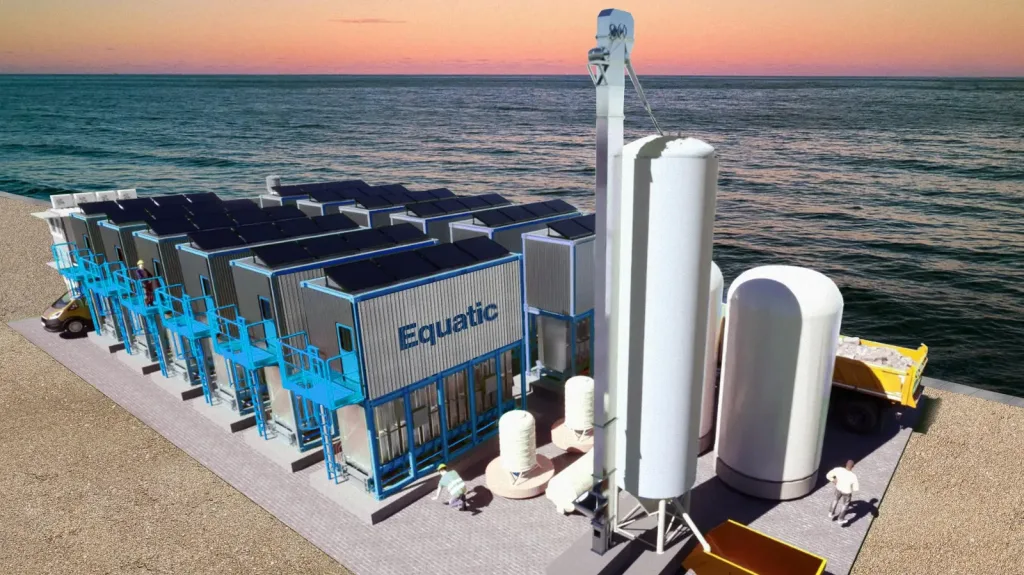

The Equatic Process, hailed as one of the best inventions of 2023, is about to undergo a major scale-up. Singapore, in collaboration with the University of California in Los Angeles (UCLA) and Equatic—a Los Angeles-based startup founded by UCLA scientists—will construct the world’s largest ocean carbon dioxide removal (OCDR) facility. This ambitious project aims to boost global climate efforts by removing carbon from the ocean and storing it in stable solids.
The Equatic Process: A Game Changer for Climate Efforts
Scientists worldwide recognise the urgent need to remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere to combat climate change. The Equatic Process offers a promising solution. Here are the key details:
1. Project Name: Equatic-1
2. Location: Singapore
3. Investment:
A joint investment of $20 million by ICM at UCLA and Equatic
4. Carbon Removal Capacity:
Equatic-1 will remove 3,650 metric tons (4,000 tons) of carbon dioxide from the ocean annually.
5. Technology:
The Equatic Process uses electrolysis to convert carbon dioxide in seawater into stable solids.
6. Storage:
The extracted carbon dioxide is stored in the form of solid calcium and magnesium-based materials, similar to how seashells naturally form. These materials remain stable for at least 10,000 years.
7. Additional Benefit:
The treated seawater pumped back into the ocean can continue to absorb more carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. Seawater holds nearly 150 times more carbon dioxide than air per unit volume.
The Path Forward
Equatic-1 is an expansion of a successful pilot program that involved smaller plants set up in Singapore and the Port of Los Angeles. These pilot plants each extracted around 100 kilograms (0.1 tons) of carbon dioxide daily. However, Equatic-1 is just the beginning. Once it fulfills its technical demonstration objectives, Equatic plans to scale and commercialise the technology globally.
When functioning at full capacity, Equatic-1 will remove the equivalent of 850 people’s annual carbon dioxide emissions. Advocates of the Equatic Process believe that ocean-based carbon dioxide removal technology can significantly contribute to the fight against climate change. However, some scientists urge further research and investment to understand both the benefits and potential ecological risks associated with this innovative approach.
In summary, Equatic-1 represents a crucial step toward a more sustainable future. By harnessing the power of the ocean, Singapore is leading the way in carbon removal technology, demonstrating that innovative solutions can make a significant impact on our planet’s health.
4. Coca-Cola Europacific Partners Plans $1 Billion Expansion in the Philippines

MANILA, Philippines — In a significant move, global beverage giant The Coca-Cola Co. has announced its commitment to invest $1 billion in the Philippines over the next five years. The expansion aims to bolster its operations and strengthen its presence in the country.
A Strategic Investment
The decision was revealed during a meeting between President Ferdinand Marcos Jr. and key executives from Coca-Cola. The company’s top brass, including Sabin Aboitiz, President and CEO of Aboitiz Equity Ventures Inc. (AEV), and Sol Daurella Comadrán, Chairperson of Coca-Cola Europacific Partners (CCEP), discussed the ambitious plans for growth.
Why the Philippines?
President Marcos expressed optimism about the expansion, citing several factors that make the Philippines an attractive market for Coca-Cola:
1. Market Potential:
With a growing population and a relatively young demographic, the Philippines offers a robust consumer base. Coca-Cola sees immense potential for its products here.
2. Strategic Location:
The Philippines serves as a gateway to the broader Asia Pacific region. By expanding operations locally, Coca-Cola can tap into neighboring markets more effectively.
3. Investment in Infrastructure:
The company is already building a new plant in Tarlac, signaling its commitment to investing in local infrastructure.
Consolidation and Distribution
Coca-Cola Europacific Partners recently completed a P100-billion buyout of Coca-Cola in the Philippines. Under this deal, AEV acquired 40 percent, while CCEP secured 60 percent ownership. As the sole distributor of Coke products in the Philippines, CCEP now holds a dominant position in the market.
The Road Ahead
Comadran, Chairperson of CCEP, emphasised the company’s enthusiasm for the Philippines: “We generate over 100,000 employees throughout our distribution network. We’re committed to investing in the Philippines and growing our business. Over the next five years, we plan to invest $1 billion, including the establishment of our new plant in Tarlac.”
With this substantial investment, Coca-Cola aims to solidify its foothold in the Philippines and continue delighting consumers with its iconic beverages.
5. Boost for UK Hydrogen as Government Backs World-Leading Industry

The United Kingdom is taking a significant stride toward a greener future by investing over £21 million in seven hydrogen projects across the country. These initiatives aim to accelerate the production of low-carbon hydrogen, a crucial component in achieving the nation’s ambitious net-zero targets. From the picturesque shores of Suffolk to the rugged landscapes of Shetland, these projects will not only produce green fuel for buses, trucks, and trains but also support local businesses in their transition away from natural gas. Let’s delve into the details of these groundbreaking endeavours that promise to reshape the energy landscape and bolster the UK’s position as a global leader in hydrogen innovation.
The companies participating in these groundbreaking hydrogen projects span a diverse range of expertise and innovation. Here are some of the key players:
1. Baker Hughes:
Known for its expertise in oilfield services and equipment, Baker Hughes will contribute its technical know-how to enhance hydrogen production and distribution infrastructure.
2. ITM Power:
A leader in electrolyser technology, ITM Power will play a pivotal role in developing efficient and scalable electrolysis systems for generating green hydrogen.
3. Orsted:
As a major player in renewable energy, Orsted will leverage its experience in offshore wind farms to explore hydrogen production using wind power.
4. Suffolk County Council:
The local government authority in Suffolk will collaborate on a project that aims to produce hydrogen from offshore wind energy, supporting the region’s transition to cleaner fuels.
5. Celtic Sea Power:
Focused on harnessing marine energy, Celtic Sea Power will explore the potential of tidal and wave energy for hydrogen production.
6. SGN:
A gas distribution network operator, SGN will investigate blending hydrogen into the existing natural gas network, paving the way for a seamless transition.
7. Eneus Energy:
This startup will work on a project in Shetland, aiming to produce hydrogen from excess wind energy, contributing to the island’s energy self-sufficiency.
These collaborative efforts demonstrate the UK’s commitment to advancing hydrogen technologies and achieving a sustainable, low-carbon future.
6. Unlocking Africa’s Economic Potential: The Operational Phase of AfCFTA Launched

Geranimo Unsplash
In a historic moment, the African Union (AU) marked a significant milestone on February 15, 2024, as the operational phase of the African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA) was officially launched. This momentous occasion took place during the 2019 July Summit in Niamey, Niger, where leaders from across the continent gathered to celebrate Africa’s commitment to economic integration and intra-African trade.
Background and Significance
The AfCFTA agreement was initially adopted and opened for signature on March 21, 2018, in Kigali, and it entered into force on May 30, 2019. The framework aimed to create a single market for goods and services, promote industrialisation, and enhance economic cooperation among African nations. With a current population of 1.2 billion people, projected to grow to 2.5 billion by 2050, the AfCFTA represents the largest free trade area since the formation of the World Trade Organisation.
Key Instruments of the Operational Phase
During the launch ceremony, several critical instruments were adopted to facilitate the smooth operation of the AfCFTA:
1. Rules of Origin:
These define the conditions under which products or services can be traded duty-free across the region.
2. Tariff Concessions:
The agreement aims for 90% tariff liberalisation, with a deadline set for July 1, 2020. Sensitive products will undergo a gradual liberalisation process over a 10-year period.
3. Monitoring Non-Tariff Barriers (NTBs):
NTBs, whether physical (such as poor infrastructure) or administrative (customs-related), hinder intra-African trade. The online mechanism will track and eliminate these barriers.
4. Pan-African Payment and Settlement System:
Ensuring timely payments in local currency and net settlements in foreign exchange at year-end.
5. African Trade Observatory:
A comprehensive trade information portal to address information gaps and provide data on opportunities, trade statistics, and exporters and importers.
Ghana’s Role and the Road Ahead
As part of the launch, Ghana was selected to host the AfCFTA secretariat, positioning itself as a hub for continental trade facilitation. The operational phase represents a bold step toward realising Africa’s economic potential, fostering job creation, and promoting sustainable development.
In summary, the AfCFTA is not merely an economic agreement; it is a transformative force that will shape Africa’s future. As the continent unites its markets, dismantles barriers, and fosters collaboration, it paves the way for shared prosperity and a brighter tomorrow.
7. Economic Prosperity: Evaluating the Winners of Free Trade Agreements

Venti Views Unsplash
In an interconnected global economy, free trade agreements (FTAs) play a pivotal role in shaping economic landscapes. These agreements facilitate the exchange of goods, services, and investments across borders, promising benefits to participating nations. But as the number of FTAs grows, it becomes crucial to assess their effectiveness and identify which countries reap the greatest rewards.
The Trade Engagement Index: Navigating the Complex Terrain
To shed light on this topic, Boston Consulting Group (BCG) has meticulously analysed over 100 economies and major trade blocs. Their research has yielded the Trade Engagement Index (TEI)—a powerful tool that compares economies based on various measures of trade engagement¹. Let’s delve into the key insights:
1. Broad-Based Coverage:
Some countries, such as the United Kingdom, Chile, Singapore, Canada, and Mexico, stand out for their comprehensive FTA coverage. These nations not only engage globally but also maintain strong ties with their regional trading partners. For instance, Mexico’s influence extends across the Americas, while Singapore thrives in Southeast Asia.
2. Strategic Selectivity:
Other economies, including the United States, the Gulf Cooperation Council states, and Taiwan, have opted for fewer FTAs. Their strategic selectivity reflects unique considerations, but it also means they operate with a narrower scope compared to the broad-based players¹.
The Stakes Are High: Why Evaluate FTAs?
As the World Trade Organisation (WTO) grapples with multilateral liberalisation, bilateral and regional FTAs have gained prominence. Governments and private-sector entities alike seek to leverage these agreements for sustained economic prosperity. But are all FTAs equally effective? BCG’s TEI provides insights for both public and private sectors:
Private Sector:
Companies armed with knowledge about governments’ FTA strengths and weaknesses can make informed investment decisions. Understanding risk profiles allows optimisation of global value chains and market access.
Public Sector:
Governments must weigh the tradeoffs of different FTA strategies. Beyond economic gains, FTAs serve as avenues for achieving diplomatic objectives, international cooperation, and even climate-change mitigation.
The Quest Continues
As we navigate an era of economic uncertainty and protectionist sentiments, evaluating FTAs becomes paramount. Join us on this exploration as we dissect the effectiveness of these agreements and uncover the true beneficiaries of free trade.
Featured image Artur Kraft Unsplash