1. Milan Innovation District Emulates Cambridge’s Success
The Milano Innovation District (MIND) is rapidly emerging as a beacon of innovation and sustainable urban development in Italy. Drawing inspiration from the renowned Cambridge Innovation Cluster, MIND is poised to become a hub for scientific excellence, technological advancement, and socio-economic growth. But what exactly makes Cambridge’s model so appealing, and how is MIND adapting these principles to its unique context?
The Cambridge Model: A Blueprint for Success
Cambridge, often referred to as “Silicon Fen,” has established itself as one of the world’s leading innovation ecosystems. Key elements of its success include:
- Proximity to a Leading University: The University of Cambridge plays a pivotal role in fostering innovation, providing a steady stream of research, talent, and collaboration opportunities.
- Strong Public-Private Partnerships: Collaboration between academia, industry, and government has been crucial in driving growth and innovation.
- Supportive Infrastructure: Cambridge boasts a well-developed infrastructure that supports startups and established companies alike, including business parks, incubators, and co-working spaces.
- Vibrant Community: The region has cultivated a vibrant community of entrepreneurs, researchers, and investors, creating a dynamic environment for innovation.
MIND: Adapting the Cambridge Model
MIND is strategically leveraging these principles to create a thriving innovation district in Milan. Here’s how:
- Academic Excellence and Research: MIND is home to the Human Technopole, a leading research institute, and the upcoming Science Campus of the University of Milan. These institutions mirror the role of the University of Cambridge, providing a foundation for cutting-edge research and innovation.
- Public-Private Synergy: The development of MIND is a result of a robust public-private partnership between Arexpo and Lendlease. This collaboration aims to create an entrepreneurial environment that fosters socio-economic growth, similar to the partnerships seen in Cambridge.
- Integrated Infrastructure: MIND’s master plan includes a mix of residential, commercial, and recreational spaces designed to support a diverse range of activities. This integrated approach ensures that the district is not just a place to work, but also a place to live and thrive.
- Community and Collaboration: MIND is designed to be a “living lab,” where different sectors can interact and collaborate. The district promotes a culture of innovation through shared spaces and events, fostering a sense of community among its residents and visitors.
Conclusion
By following the Cambridge model, MIND is setting the stage for a new era of innovation in Milan. The district’s focus on academic excellence, public-private partnerships, integrated infrastructure, and community engagement positions it as a key player in the global innovation landscape. As MIND continues to grow, it will undoubtedly contribute to Milan’s reputation as a center of scientific and technological progress.
2. Hong Kong and Peru Sign Free Trade Agreement

chelsea-cook
Lima, Peru – November 15, 2024 – In a significant move to bolster economic ties, Hong Kong and Peru have signed a comprehensive Free Trade Agreement (FTA) on the sidelines of the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) Economic Leaders’ Meeting. The agreement was signed by Hong Kong’s Secretary for Commerce and Economic Development, Mr. Algernon Yau, and Peru’s Minister of Foreign Trade and Tourism, Mrs. Úrsula Desilú León Chempén, in the presence of Hong Kong’s Chief Executive, Mr. John Lee, and Peru’s President, Ms. Dina Boluarte.
Strategic Importance
This FTA marks the first such agreement signed by the current-term Hong Kong Special Administrative Region (HKSAR) Government, highlighting its strategic importance. Mr. Lee emphasised that the agreement would open up the Peruvian market to Hong Kong’s manufacturers, service providers, and investors, providing legal certainty and better conditions for business operations.
Key Provisions
The FTA covers a wide range of areas including trade in goods and services, investment, electronic commerce, and dispute settlement. Notably, Peru has committed to eliminating tariffs on approximately 98.3% of its tariff lines for Hong Kong’s originating goods, with 91.3% of these tariffs being eliminated immediately upon the agreement’s entry into force. This is expected to enhance the competitiveness of Hong Kong products in the Peruvian market.
Economic Impact
Bilateral trade between Hong Kong and Peru has been growing steadily, with merchandise trade amounting to HK$5.2 billion in 2023. The FTA is anticipated to further boost this growth by providing a transparent and predictable trading environment. It also aims to create new business opportunities and enhance bilateral investment flows, contributing to the economic growth of both regions.
Future Prospects
The agreement also sets the stage for future cooperation, with negotiations for a separate Investment Promotion and Protection Agreement (IPPA) already underway. This will further strengthen the economic partnership between Hong Kong and Peru, enabling both sides to capitalise on new development opportunities.
Conclusion
The signing of the FTA between Hong Kong and Peru is a landmark event that underscores the commitment of both regions to fostering closer economic ties. With its comprehensive scope and high-quality commitments, the agreement is poised to bring significant benefits to businesses and investors, paving the way for a prosperous future.
3. Thailand-South Korea Economic Partnership Agreement

In a significant development for regional trade, Thailand and South Korea are on the verge of finalising their Economic Partnership Agreement (EPA). This agreement, expected to be signed during the 36th APEC summit hosted by South Korea next year, aims to enhance economic cooperation between the two nations.
Strengthening Economic Ties
The EPA is set to build on existing agreements such as the ASEAN-Korea Free Trade Agreement (AKFTA) and the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP). According to Thailand’s Commerce Minister Pichai Naripthaphan, the new agreement will expand markets for goods, services, and investments, fostering deeper economic integration.
Key Areas of Collaboration
The agreement will focus on several key sectors, including digital trade, supply chain management, and high-quality agricultural products. Thailand has requested South Korea to open its market to products like mangos, mangosteens, pineapples, and processed seafood. Additionally, Thailand is encouraging South Korean investments in its target industries, such as electric vehicles, semiconductors, and biotechnology.
Economic Impact
In 2023, South Korea was Thailand’s 12th largest trade partner, with a trade value of $14.74 billion. This included $6.07 billion in Thai exports and $8.67 billion in imports from South Korea. The first nine months of 2024 saw bilateral trade reach $11.47 billion, highlighting the growing economic interdependence between the two countries.
Future Prospects
The EPA is expected to address challenges in trade and investment, with plans to resume the Joint Trade Committee ministerial meetings early next year. This will further facilitate economic activities and strengthen the partnership between Thailand and South Korea.
As both nations prepare to finalise this landmark agreement, the future looks promising for enhanced economic collaboration and mutual growth.
4. India-US Trade Under the New US Regime
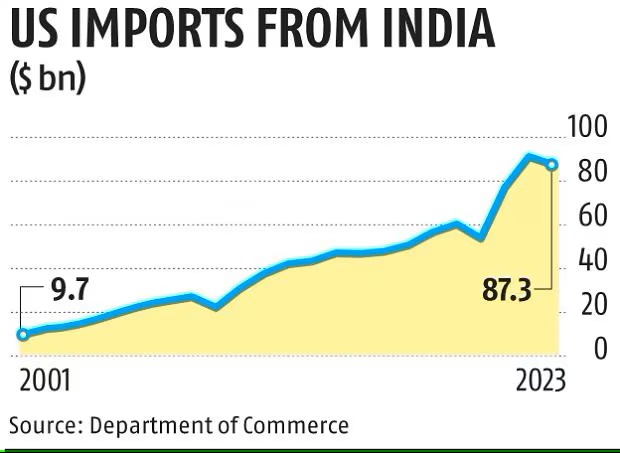
s the United States transitions to a new administration, the dynamics of India-US trade relations are poised for potential shifts and opportunities. Historically, the trade relationship between these two nations has been robust, characterised by significant growth and mutual benefits across various sectors.
Current State of India-US Trade
India and the United States have seen their bilateral trade in goods and services surpass $200 billion in 2023. This growth has been driven by strong economic ties and a series of strategic agreements aimed at enhancing trade and investment. The recent 14th Ministerial-level meeting of the India-United States Trade Policy Forum (TPF) highlighted the progress made in resolving longstanding trade disputes and improving market access.
Key Areas of Focus
- Critical Minerals and High-Tech Products: Both nations have identified critical minerals and high-tech products as key areas for enhanced cooperation. This includes developing a roadmap for collaboration to achieve economically meaningful outcomes.
- Supply Chain Resilience: The new administration is expected to continue focusing on supply chain resilience, particularly in sectors like pharmaceuticals and IT hardware. This aligns with India’s goals of diversifying its supply chains and reducing dependency on single sources.
- Digital Trade and Technology: The digitalisation of trade documents and the adoption of high-level principles on digital trade are areas where both countries can collaborate further. This will streamline trade processes and reduce barriers.
Potential Challenges
While the overall outlook for India-US trade remains positive, there are potential challenges that could arise with the new administration’s policies. For instance, the emphasis on “America First” could lead to higher tariffs on certain goods, impacting sectors like automobiles, textiles, and pharmaceuticals.
Additionally, changes in visa policies could affect the IT services sector, which heavily relies on the US market.
Opportunities for Growth
Despite these challenges, there are numerous opportunities for growth in India-US trade relations:
– Renewable Energy and Biofuels: The US has welcomed India’s initiatives in renewable energy, including the reduction of timelines for ethanol blending and the launch of the Global Biofuels Alliance. These areas present significant opportunities for collaboration and investment.
– Healthcare and Pharmaceuticals: Both countries are committed to ensuring the availability of safe and effective medical products. Increased inspections by the US FDA in India and collaboration on medical device standards can enhance trade in this sector.
– Agricultural Trade: The finalisation of the Turtle Excluder Device (TED) design and its implementation can boost seafood trade between the two nations while promoting sustainable practices.
Conclusion
The future of India-US trade under the new US regime looks promising, with both nations committed to deepening their economic ties. By focusing on key areas of mutual interest and addressing potential challenges proactively, India and the United States can continue to build a strong and resilient trade relationship that benefits both economies.
5. EBRD and International Bank of Azerbaijan Partner to Expand Trade Finance

In a significant move to bolster trade finance in Azerbaijan, the European Bank for Reconstruction and Development (EBRD) has approved a trade finance limit of up to $50 million (€46.7 million) for the International Bank of Azerbaijan (IBA). This inaugural agreement was signed at the United Nations Climate Change Conference (COP29) in Baku on November 14, 2024.
The new facility, established under the EBRD’s Trade Facilitation Programme (TFP), aims to support export and import operations for private clients, thereby enhancing Azerbaijan’s integration into global markets. The EBRD’s TFP currently operates in 27 economies, with a network of over 125 issuing banks and more than 800 confirming banks.
Strengthening Trade and Green Initiatives
EBRD President Odile Renaud-Basso emphasised the value this trade finance line will add to Azerbaijan’s financial sector and its clients. She highlighted the EBRD’s commitment to advising IBA on identifying and structuring green transactions. This aligns with the broader goal of supporting projects focused on the green economy and reducing carbon emissions.
Abbas Ibrahimov, Chairman of the Management Board of IBA, expressed the bank’s dedication to utilising these financial resources to support green trade projects. He reiterated IBA’s commitment to maintaining a safer and cleaner environment.
A Boost for Azerbaijan’s Financial Sector
This partnership is a testament to the EBRD’s increasing support for Azerbaijan’s financial sector. The EBRD has been a leading institutional investor in Azerbaijan, having invested over €3.7 billion through 191 projects to date. The new trade finance limit will further strengthen Azerbaijan’s export and import operations, providing local businesses with greater access to international markets.
Conclusion
The collaboration between the EBRD and IBA marks a significant step towards enhancing trade finance in Azerbaijan. By focusing on green trade projects and expanding trade transactions, this partnership will not only benefit the financial sector but also contribute to a more sustainable and integrated global economy.