1. The Ukraine Crisis and International Trade – Possible Causes and Effects
Some of the possible effects that could be experienced in international trade due to the Russian invasion of Ukraine on 24 February
- Sanctions – the US and UK. UK initially sanctions target Putin and his executive team directly however the latest announcement says the UK Government will extend sanctions to further restrictive economic measures by targeting the Central Bank of Russia. Since then the UK, US, Canada, Spain, Germany and now Italy have blocked some Russian banks from payments on the international payment system Swift which would effectively block Russian imports and exports.
- Energy prices – energy prices are due to rise in the UK from April anyway. The conflict could heighten prices further as Crimean gas pipeline currently recognized as the belonging to the Ukraine becomes even more contested. Europe gets 40% of its gas & 25% of its oil from Russia via the pipeline. Fuel could move up beyond £1.50 a litre in the UK soon says the RAC.
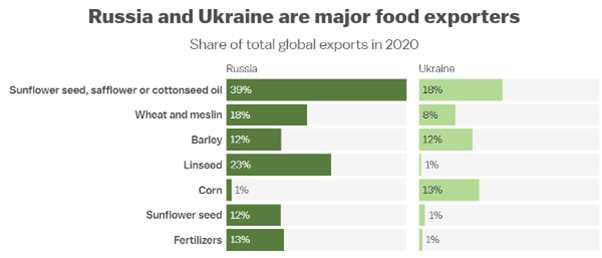
- Food prices – Russia is the world’s largest supplier of wheat. Russia and the Ukraine account for 25% of global food exports including 57% of the global export of sunflower seed, safflower or cottonseed oil. Global food prices are already at their highest rates since 2011 and climbing.
- Stocks – gold is at its highest price in 13 months. Other indices The S&P 500 dropped 10% from its recent peak. Defence stocks are winners.
- Business – any organisation with a base or deep investment in Russia could be disadvantaged such as BP, Shell, Jaguar Landrover, BAT, Renault and Carlsberg.
The Institute of Export and International Trade are hosting a free webinar 11am-12pm this Wednesday 2 March on companies can comply with Trade sanctions against Russia. Register here.
2. EU White-lists Mauritius

The EU has announced that Mauritius is now on the OECD white list. It was declared a high risk third country due to money laundering and terrorist financing risk but has changed status due to advances in anti-money laundering and counter terrorist financing laws as well as other compliance advances. It is no longer deemed an uncooperative tax jurisdiction. The change will improve Mauritius as a financial services industry destination and increase investment destination as well as possible domicile for cross-border investment into Africa and Asia.
Trade Horizons
Trade Horizons is an award-winning market entry company, assisting ambitious companies to identify, develop and grow sustainable revenues in new geographic markets. We offer support to clients in international strategy development for their global business growth, and throughout the key phases of market entry execution – Preparation, Launch and Growth. Click here to find out more.
3. EU Accelerates Indo-Pacific Relations

The EU met with leaders of 30 Indo-Pacific countries in Paris to discuss maritime cooperation with the purpose of increasing engagement in the Indo-Pacific region and the EU, we suppose for easier faster trade routes.
It follows America’s Indo-Pacific strategy published on 11 February which states a commitment to strengthen capacities of the US & allies throughout the region and specifically calls out China for its aggression towards certain nations in the region such as coercion against Australia, the conflict along the Line of Actual Control with India, growing pressure on Taiwan, and tensions in the East and South China Seas.
The region is home to 60% of global wealth and population.
4. Digital Trade Revolution for Europe
The G7 voted to adopt digital systems for global trade in May last year and gave countries 12-18 months to get ready for the changes however Germany has still not adopted digital documents due to a lack of clarity about the term ‘functional equivalence’ stated in the Directive.
A report by the ICC says digitisation could add US$9 trillion and Germany could realise €1.1tn in extra exports of that by 2026 however Germany is lagging due to an unclear definition of ‘functional equivalence’ for electronic trade documents which is important as this is necessary for the bill of lading as well as warehouse receipts & consignment notes.
It needs to align with the United Nations Commission on International Trade Law (UNCITRAL) Model Law on Electronic Transferable Records (MLETR) which states that a digital document is equivalent to their paper counterpart.
Paper bills of lading are the single most important document in the shipment of goods however they are prone to error, fraud, delay, are expensive & inefficient and environmentally not as sustainable as digital documents.
5. UK signs historic trade deal with Singapore

The new New Digital Economy Agreement (DEA) will cut costs and regulations for bilateral trade between UK & Singapore. The agreement in principle was reached to encourage new trade opportunities between the two countries which is currently valued at £16 billion. Both countries excel in services, this trade deal is expected to impact finance, advertising and engineering.
Trade Horizons CEO Nick Jordan said
“The UK-Singapore Digital Economy Agreement (DEA) is the first for a European nation and designed to strengthen the trading relationship between the two countries. It ends outdated rules that affect both goods and services exporters, making it easier for UK business to target new opportunities in both Singapore and the wider region.”